Introduction to Verisense
Verisense is an infrastructural protocol for the agentic network, enabling true AI autonomy and interoperability on a decentralized foundation.
Why Verisense? The Challenge for AI and Blockchain
Today's AI and blockchain technologies are powerful but siloed.
Traditional blockchains are secure and decentralized but face critical limitations: * Limited to Deterministic Computation: Blockchains can't perform input/output (I/O) operations, like making an API call. This isolates them from the real-world data essential for AI. * Cryptographic Fragmentation: Different blockchains use different signature schemes, making it difficult for them to communicate and work together. * Cost-Complexity Trade-off: Higher security and decentralization come at a higher cost, forcing developers to compromise on either security or affordability.
AI agent protocols (like A2A and MCP) are advancing rapidly but lack the foundational trust, identity, and coordination layers needed to create a truly open and interoperable network. They face challenges with service discovery, multi-agent coordination, and verifiable identity.
Verisense is designed to bridge this gap. It's an innovative blockchain solution built to be the backbone of the new agentic network, providing a flexible, interoperable, and cost-effective framework where AI agents can securely and autonomously interact.
The Verisense Architecture: A Dual-Layer Network
Verisense uses a unique dual-layer model to overcome the limitations of traditional blockchains.
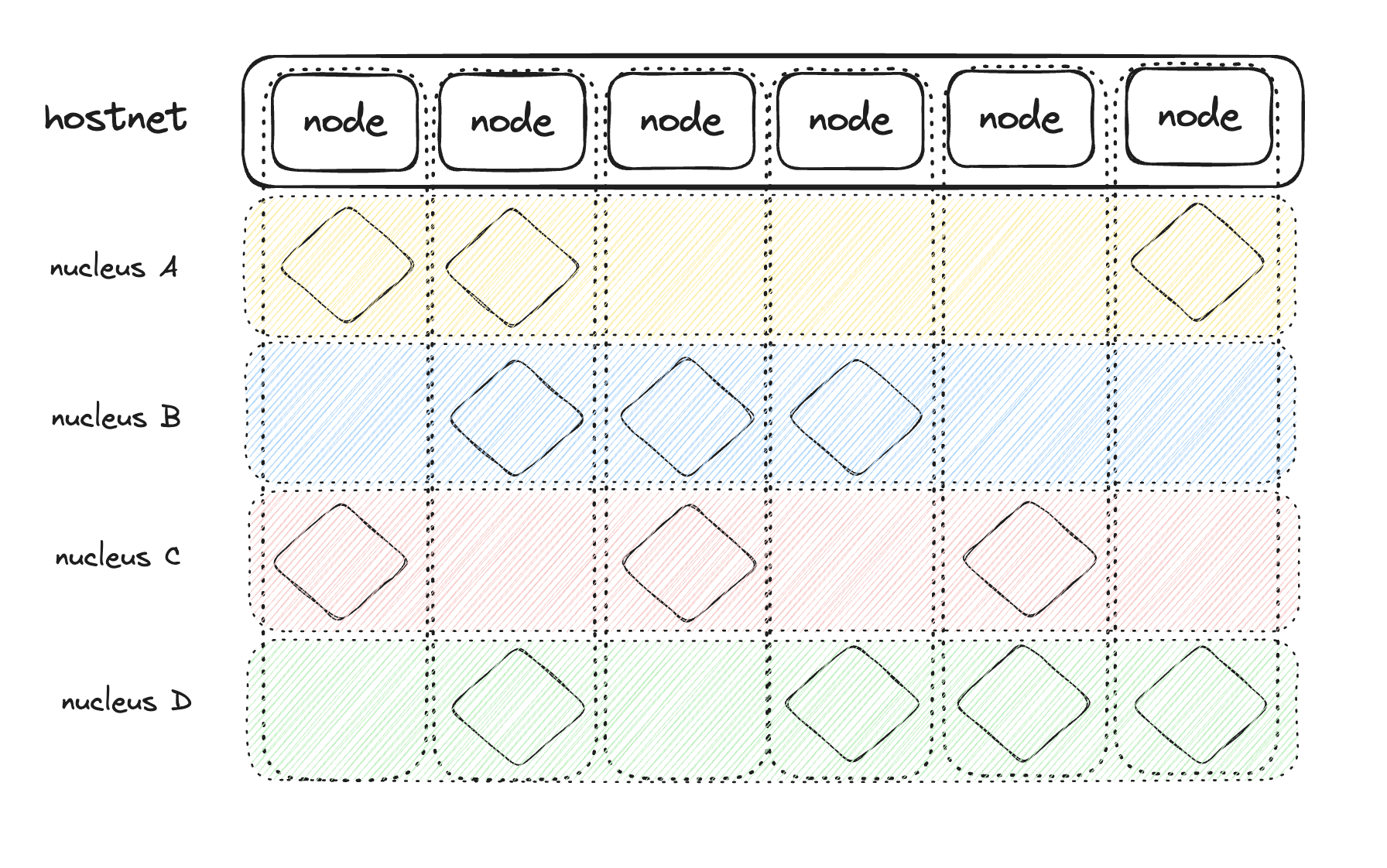
1. The Hostnet
The first layer, the Hostnet, is a secure and robust Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network built with Substrate. It acts as the coordination and security backbone of the entire system. Unlike other blockchains, the Hostnet does not run complex smart contracts. Instead, it delegates all application logic to the second layer.
2. The Subnet and Nucleus
The second layer is a dynamic network of Subnets. A Subnet is a smaller, independent network composed of a select group of Hostnet validators.
Within each Subnet runs a Nucleus—the Verisense equivalent of a dApp or smart contract.
This architecture allows developers to define the exact requirements for their application: * Custom Consensus: A Nucleus can choose the number of validators it needs, balancing cost and security. * High Performance: By operating in a smaller consensus group, a Nucleus can achieve much higher performance and efficiency than a traditional dApp. * Scalability: Each Nucleus runs in its own isolated environment, preventing network-wide congestion.
Beyond Smart Contracts: What a Nucleus Can Do
A Nucleus is more than just a smart contract. It's a powerful, serverless execution environment with capabilities designed for the AI era:
- Active Network Requests: A Nucleus can make HTTP requests, allowing it to interact with any external API, data source, or Large Language Model (LLM).
- Multi-Type Threshold Signatures (TSS): A Nucleus can hold private keys for different blockchains (like Bitcoin and Ethereum) and sign transactions. This enables true, bridgeless cross-chain interoperability.
- Timers: A Nucleus can schedule future or recurring tasks, enabling automation and time-based logic.
- Reverse Gas Model: Unlike traditional blockchains where users pay for transactions, Verisense allows developers to cover the operational costs, creating a frictionless Web2-like experience for end-users.
By combining a flexible, cost-effective architecture with powerful, I/O-enabled applications, Verisense provides the foundational layer for building the next generation of decentralized AI agents and applications.